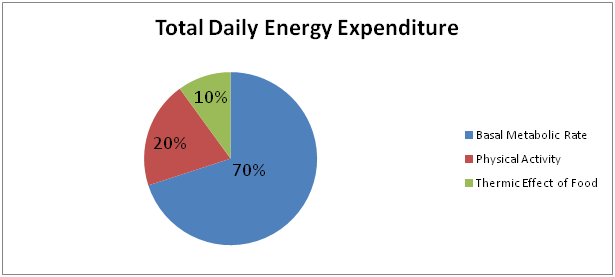Whenever we see a thin-looking person eat a lot, we can hear people saying, “Ah, he/she must have a great metabolism.”A common question might pop up in our minds, “What exactly is this metabolism?” In layman terms, metabolism can be defined as a balance between the reactions that build things up, in other words, anabolism, and the reaction that break things down, i.e. catabolism.
In a typical catabolic process, the carbohydrates are metabolized into sugar, proteins into amino acids and fats into fatty acids. On the other hand, examples of anabolism are the building of muscles and storage of glucose as glycogen and fat as adipose tissues. Also, all repair and renewal mechanisms are part of anabolism.
There are a few terminologies/definitions that one needs to know for solving the weight loss puzzle.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
BMR is the amount of energy our body burns while resting in a temperate environment. This energy is used to support most of the basic functions of the human body like breathing, blood circulation, brain and nerve functions, and support of vital organs.
BMR is responsible for maintaining a state of homeostasis in your body. Generally, BMR accounts for 70 percent of total daily expenditure, physical activity accounts for 20-25 percent, and digestion only for 5-10 percent. Our BMR is largely determined by our age, sex, genes, and the balance of hormones in our body.
Total Energy Expenditure, BMR, and the notion of stable BMR
What’s the best way to beat obesity? Exercise?! Well, there is more to it.
Total Energy Expenditure is the sum of BMR, energy used for digestion, non-exercise activities, excess post-exercise oxygen consumption, and exercise. It is the sum total of all the energy used by the body.
Against the general notion that BMR remains stable, experiments have shown that the total energy expenditure can go up or down by as much as 50 percent depending on calorie intake as well as other factors.
Exercises are important but they contribute only 5-10 percent to obesity story. Obesity is largely driven by the hormones. Exercises help by building muscles. More muscles lead to more calorie burning and increase in BMR.
Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Weight Set Point
As stated earlier, the body works on the biological principle of homeostasis, which also means maintenance of stable conditions. Any changes in the body weight are balanced by the compensatory changes in the BMR and other body parameters. The principle of homeostasis, further, explains the concept of set body weight that works to keep the body weight as close to this set weight as possible.
This is the reason when the weight drops below the body set weight, the BMR also falls to conserve energy and to get back the body weight to the set weight. However, the problem in obesity is that the set weight is way too high. To counter the compensatory mechanism in weight loss, we need to first understand how the set point is actually set and how it can be changed.
Understanding the Set Point
Do you know that the hypothalamus region of the brain is responsible for setting an ideal weight? Yes, this region of our brain sets the ideal weight by integrating signals regarding energy intake, energy expenditure, and hormonal activities. This is the reason why hypothalamic damage results in intractable weight gains in humans. Obesity is not a problem of calorie-in and calorie-out but a hormonal imbalance in which insulin plays a primary role. It is the level of insulin in your body that determines your set weight.
How High Insulin Levels and Insulin Resistance regulate the set-point?
Insulin resistance is not something that you get in an overnight time frame. It develops over a period of time when a high carbohydrate, refined sugar, fructose diet or high levels of stress hormones makes the cells develop immunity towards insulin and refuse access to sugar. Since the main job of the insulin is to unlock cells for glucose to get in, the pancreas increases the production of the insulin. High insulin leads to more insulin resistance, which, in turn, leads to more insulin production. This self-fueling vicious cycle wreaks havoc on the fat cells.
To know more about Insulin resistance read SoulGuru’s article High insulin is responsible for many chronic conditions
The liver in the presence of high insulin converts excess carbohydrates and fructose into triglycerides. These fatty acids get deposited in the liver and other tissues as visceral fat. While the production and deposit of fat increases in the body, the retrieval of fat for energy slows down. The high anabolic role of insulin makes it difficult for the opposite hormones to play their catabolic role of breaking down fats. This slow process of accumulation of a few kilograms of weight every year gradually increases the body’s set weight.
Solving the weight loss puzzle- Break the cycle of high insulin and insulin resistance to reduce the set point
To reduce the set point, one needs to understand that it is the persistent high insulin levels that have led to the development of insulin resistance. The solution lies in breaking this vicious cycle of high insulin and insulin resistance. This can only be achieved by keeping the insulin levels low for longer periods of time by making changes to what we eat and when we eat. You can achieve this by modifying your diet to include food items that have limited effect on insulin and excluding foods that spike up the insulin. At the same time, you can increase the gap between eating so that insulin can remain low for the extended period of time and allow catabolic hormones to play their part.
What to eat and what not to?
One of the major steps that you can take to achieve good metabolism and, in turn, reduce obesity is to eat right.
Stop eating processed and refined food – Limit your carbohydrates
Food that has refined carbohydrates and sugar spike up both the insulin and glucose levels in the blood. Junk foods that are rich in high fructose corn syrup are very bad for health. Non-fruit fructose can directly cause insulin resistance. Choose whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and fruits that are rich in fiber. Fiber helps to lower the glycemic index of food and has a lower effect on insulin as well. Total carbohydrates intake must be limited to around 25-40 percent depending on the severity of our problem.
Take more plant-based protein
Moderate amounts of proteins must be consumed. And, it is advisable to prefer plant-based proteins as they have a lower impact on the insulin levels. Also, proteins help to keep your stomach full for a longer period of time because of longer time required for digesting them. Though artificial proteins found in whey products and protein shakes need to be avoided as they hike the insulin levels. Overall proteins intake can account for about 25 percent of our diet.
Increase the consumption of healthy fats
Fat has minimal effect on insulin and that is the reason that many experts on weight loss particularly Dr. David Ludwig and Dr. Jason Fung are promoting low carbohydrate high-fat diet to circumvent the impact of high insulin. Avocado, olive oil, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, and saturated fats, like butter, cheese, coconut oil, and ghee can be included in the diet. The high-fat diet, not only shows the minimal effect on insulin levels but also provides long-lasting satiety and hence helps to increase the gaps between meals. While going on a high-fat diet, extreme care should be taken to keep the trans-fats and vegetable oils completely out of the diet program. The fat can constitute about 30-50 percent of your diet.
When to eat?
Once you know what to eat, the second biggest challenge is about knowing and implementing when to eat.
Guiding Principle
Obesity is caused by two interlinked phenomenon – high insulin and insulin resistance. Most of the dieting programs control the incidence of high insulin through eating right kind of food. However, they do not take into account insulin resistance and its adverse effects. Due to this reason, most weight loss programs fail. In other words, after an initial, drastic weight loss, one gains back all the weight. Therefore, without tackling the underlying cause of insulin resistance, you cannot permanently shave the extra weight off.
Increase gaps between meals to break insulin resistance
Insulin resistance can only be broken by long stretches of very low insulin levels. That can be achieved by
- Increasing the gaps between meals to 4-5 hours. Don’t constantly keep munching food. Against the general notion, eating every two hours only gives the minimal benefit of marginally increasing your metabolic rate but causes maximum weight gain by constantly keeping your insulin levels high.
- Going on intermittent fasting for 14-16 hours, i.e. after the evening supper at 6 PM, one can have breakfast next morning at 8 AM.
- Practice complete fasting for 1-2 days in a week depending on our capacity and medical conditions. Alternatively, it is advisable to join any naturopathy center where fasting is a part of the treatment regimen.
Snacking in between the meals need to be completely stopped though beverages in moderate amounts like tea, coffee, lemon water, etc. can be taken.
Ketosis and fat burning
By following this rigorous process you can activate our catabolic hormones like glucagon to break the stored sugar. This can also help the growth hormones to increase the availability and utility of fats for fuel. Activation of adrenalin hormone helps you to rev up the basal metabolic rate. A study has shown that 48 hours of fasting produces a 3.6 percent increase in basal metabolic rate. Your body would go into ketosis and start burning fat for energy. This way you can constantly lower your body set-weight and achieve lasting weight loss that addresses the root causes of high insulin and insulin resistance. Solving the weight loss puzzle was never so easy.